By Suchitra Sriram
The trend of the Asia Pacific solar PV systems market indicates augmenting demand from countries such as Australia, Japan, South Korea, Thailand, Malaysia, and the Philippines because of the strong government commitment towards promoting solar PV power and in creating sustainable cities. Inadequate utility power infrastructure in countries such as Indonesia, Vietnam, the Philippines and the rest of Southeast Asia (comprising Laos, Cambodia and Myanmar) provide excellent growth opportunities for installing solar PV systems under the various remote and rural electrification programs.
The market being highly price competitive, it is essential for system integration companies to focus on enhancing its growth through its strong technical workforce, provision of high quality PV components, to deal with extensive renewable energy systems, undertake on-time delivery of projects, and provide effective value-added maintenance services.
North Asia: Strong Government Support
Very high end-users’ inclination towards adopting clean energy technologies, mainly in Japan and South Korea, for electrifying homes and business enterprises has led to a tremendous market for solar Photovoltaic (PV) systems. Furthermore, strong government support through policies, feed-in tariff schemes and other deployment programs have resulted in massive adoption of solar PV systems both for on-grid and off-grid application in North Asia. Solar PV is likely to be the most preferred renewable energy technology in the region to combat climate change.
Market Drivers
North Asian solar PV systems market earned revenues of US$1,951.6 million in 2009 and is estimated to reach US$3,582.5 million in 2016 due to massive adoption of solar PV systems as result of an attractive feed-in-tariff scheme, the global decline in prices, and robust government support for the use of solar power.
The presence of attractive feed-in tariff in Japan and South Korea and the introduction of the Renewable Energy Development Act in Taiwan are expected to propel the market for on-grid solar PV system installations for both distributed and centralized solar power plants. As the countries have fixed targets to reduce emissions as per the Kyoto Protocol, several measures are underway to achieve it.
Market Inhibitors
However, market penetration of solar PV systems has been challenged by the high cost of installation that makes it unaffordable for an average end user. Thus, market growth is heavily dependent on government support in terms of policy guidelines, tax credits, subsidies or rebates. Moreover, the well-developed power infrastructure deters the use of solar PV systems in some urban areas.
Besides high installation costs, the credit crunch due to the global financial crisis affected the economic viability of many solar power projects in the region. Small companies with weak cash flows were severely affected because of the slowdown. This resulted in major markets such as South Korea introducing a cap on annual installations which to a certain extent impacted the regional market revenues in 2009.
Growth Momentum
In order to sustain the growth momentum of solar PV systems market in North Asia, it is pertinent for governments to continue their support for this industry till the price reaches grid parity. Higher budget allocation for research and development, decrease in production costs and improving end users’ awareness about the benefits of this technology would pave way for large-scale commercialization. This, in turn, has the capacity to attract new companies into the market.
Overall, North Asian countries have led the Asia Pacific region in terms of early adoption of solar PV systems as well as in developing a very strong production base that caters to world demand.
Sustaining this growth momentum calls for involvement across all the stakeholders from the government, manufacturers, research institutes, system integrators and end users. Solar PV systems’ ability to alleviate carbon emissions combined with long-term reduction in maintenance costs demonstrates the immense market potential of this technology.

Figure 1. Asia Pacific total solar PV systems market (2009)
Southeast Asia: Follows Global Trend
Solar PV systems provide the ideal environment-friendly power generating solution for electrifying remote rural areas in power deficient areas of Southeast Asia as it is neither technically nor economically viable to extend grid coverage to certain isolated areas. In addition, urban end users’ growing preference towards adopting sustainable energy solutions has accelerated the adoption of solar PV systems, particularly for rooftops and buildings. Furthermore, strong government support through policies, feed-in tariff schemes and other deployment programs have resulted in gradual uptake of solar PV systems both for on-grid and off-grid application.
Market Drivers
Southeast Asian solar PV systems market earned revenues of US$99.6 million in 2009 and is estimated to reach US$254.8 million in 2016 due to increasing awareness about environment-friendly power generating technologies, global decline in prices, strong government support for renewable energy and use of solar power for rural electrification purposes.
Favorable topography with adequate solar radiation throughout the year coupled with policies and regulations from the government are likely to expand market opportunities during the next five to seven years in Southeast Asia especially in countries such as Thailand, Malaysia, and the Philippines. The introduction of feed-in tariff is expected to be a big stimulant for on-grid solar PV system installations for both distributed and centralized solar power plants.
Market trends indicate burgeoning demand owing to strong governmental commitment to the promotion of solar energy and creation of sustainable cities. Besides increasing commitment from local governments, solar PV systems for rural electrification projects are likely to be driven by active participation of non-governmental organizations and availability of funds from international financial agencies, and involvement of local communities.
Market Inhibitors
However, market penetration of solar PV systems has been challenged by the high cost of installation as the majority of customers fall under the low-income group. Thus, market growth is heavily dependent on government support in terms of policy guidelines, tax credits, subsidies or rebates. Solar PV systems market growth will continue to rely on government support until the price reaches grid parity. Moreover, the well-developed power infrastructure deters the use of solar PV systems in some urban areas.
The global financial crisis did not have a major impact on the solar PV systems market in Southeast Asia. However, due to the ripple effects of the financial crisis on the key global solar power markets, the economic viability of some PV projects diminished because of lack of credit from banks, financial agencies and donor countries. Weak economic conditions have prevented customers from installing expensive onsite power projects. Another factor that contributed to restrained market momentum was the extensive use of diesel fired generator sets and other low-cost renewable energy technologies.
Growth Momentum
To rev up the pace of growth of the solar PV systems market in the Asia Pacific region, it is vital for countries to establish realistic targets, streamline the policy framework, and aggressively boost customer awareness. Going forward, as production costs decline and solar PV systems gain traction, installation costs are expected to reduce and pave the way for large-scale commercialization. This, in turn, will attract new entrants across the solar industry value chain.
Considering the highly competitive nature of the market, it is imperative for system integration companies to focus on enhancing growth by establishing a strong technical workforce and providing high-quality PV components. Also, participants must ensure on-time delivery of products and provide superior value-added maintenance services to outpace competition.
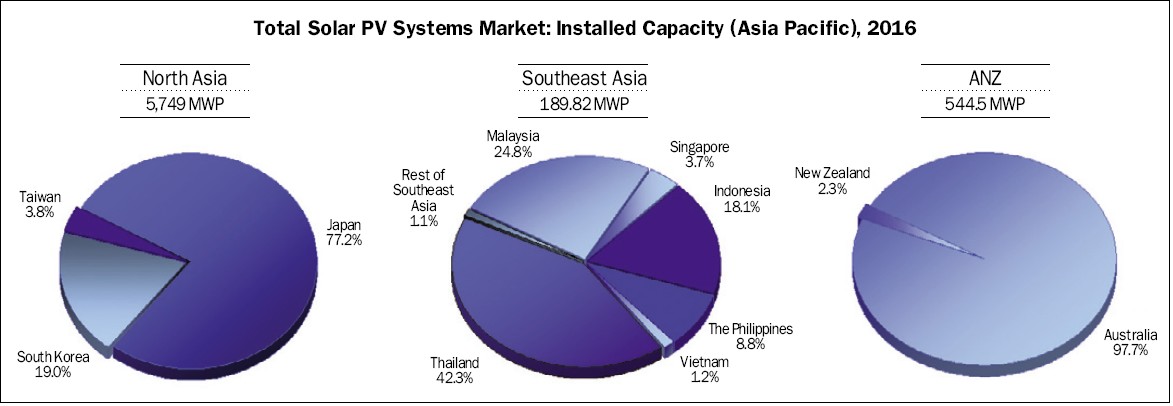
Figure 2. Asia Pacific total solar PV systems market forecasts (2016)
Australia & New Zealand: Preference for Clean Energy
Volatile oil prices combined with heightening concerns over global warming have paved way to the successful deployment of solar PV systems both in urban and remote areas in the Australia and New Zealand (ANZ) region. Solar PV systems provide the ideal environment-friendly power generating solution for electrifying remote rural areas as it is neither technically nor economically feasible to extend grid coverage across the vast territories.
Market trends indicate burgeoning demand owing to strong governmental commitment to the promotion of solar energy and creation of sustainable cities. Besides increasing commitment from the local government, solar PV systems for rural electrification projects are likely to be driven by active participation of non-governmental organizations and availability of funds from international financial agencies, and involvement of local communities.
Market Drivers
ANZ solar PV systems market earned revenues of US$198.2 million in 2009 and is estimated to reach US$827.8 million in 2016.
Growing environmental consciousness and the urgent need to act against soaring carbon emission levels have forced governments to put forth policies and programs that address this mounting challenge. As a result, introduction of the solar cities program, solar credits program, solar flagships programs and various other renewable energy programs encompassing solar PV technologies have rapidly encouraged adoption as well as attracted new entrants into the lucrative ANZ region. The topographical advantage of the region, especially Australia with its very high solar (direct sunlight) radiation, has also led to new growth opportunities in the solar thermal market.
The introduction of feed-in tariff is expected to be a big stimulant for on-grid solar PV system installations for both distributed and centralized solar power plants. State-wise solar PV targets too have led to increasing demand for solar PV systems. In many remote locations, solar PV systems are largely promoted along with diesel fired generator sets to satisfy on-site power needs of small communities.
Market Inhibitors
However, market penetration of solar PV systems has been challenged by the continued dominance of coal in the overall electricity mix. The ANZ region, especially Australia, is the world’s fourth largest producer of coal and has estimated reserves of 76 billion tonnes. In addition, well-developed and stable power infrastructure restricts the usage of solar PV systems in urban areas.
In several cases, adoption of expensive solar PV systems becomes only a secondary option as there are several other low-cost distributed power generation technologies that satisfy the on-site power requirements of the end users. Direct threat arises from the proven, low-cost and easily available diesel fired generator sets and wind power systems.
Solar PV systems market growth will continue to rely on government support until the price reaches grid parity. This includes the government’s introduction of a uniform gross feed-in tariff scheme at a national level.
Growth Momentum
Information dissemination from the concerned government agencies about the proposed projects, favorable locations for installation, existing approval processes, and technical guidelines needs to be readily available to prospective project developers and end users. In few Australian states and in New Zealand, aggressive measures need to be adopted to increase the overall awareness levels about the long-term benefits of solar PV power systems.
Suchitra Sriram is Program Manager of Frost & Sullivan (www.frost.com), a global growth consulting company. Frost & Sullivan has been partnering with clients to support the development of innovative strategies for more than 40 years.
For more information, please send your e-mails to pved@infothe.com.
ⓒ www.interpv.net All rights reserved
|